
for prokaryotes, it is the operons that regulate the process. In eukaryotes, different transcriptional factors regulate the transcription process. Protein elongation takes place through the binding of amino acids. RNA sequence’s elongation happens by way of binding the complementary base pair to the new sequence. Raw materials such as adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine. It occurs after the transcription process. It occurs before the translation process. Although it is the second step, it is of utmost importance as it concludes the process of gene expression. Translation always follows transcription. It is the first and most important step in gene expression. The process of translation is particularly confined in the cytoplasm. The process is closed by blocking the RNA polymerase. The whole process is protein-regulated and functions mainly as signals. It happens in the ribosomes linked to the endoplasmic reticulum. It follows a complementary base pairing DNA rules. (8, 9)Įukaryotes’ RNA polymerase is unique and complex.

Various factors control the translation process such as the enzyme aminoacetyl tRNA synthetase. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme catalyzes and regulates the entire process. Transcription happens when there is a need for a specific gene product for a particular tissue. The expression of RNA leads to forming a polypeptide chain. (7)Īntibiotics that inhibit translation are chloramphenicol, anisomycin, tetracycline, cycloheximide, puromycin, erythromycin, and streptomycin. The process of transcription can be inhibited by certain types of antibiotics, specifically rifampicin and 8-hydroxyquinoline. The site of the translation process is the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and ribosomes in eukaryotes. The transcription phase takes place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and the nucleus of eukaryotes. The meeting leads to the dissociation of the ribosome causing the release of the polypeptide. The signal that the termination phase is about to happen is when the ribosome meets one of the three stop codons. The end phase is marked by the release of RNA transcript and detachment of polymerase from the DNA. The translation phase begins when the ribosome subunits, tRNA, and initiation factor bind to mRNA. The transcription process is triggered to start upon the binding of RNA polymerase proteins to DNA promoters a substance that directs the location of the initial phase of transcription. Micro RNAs or non-coding RNAs, rRNA, mRNA, and tRNA. The step is called translation because it translates what is written in the mRNA template. Transcription is a process by which the genes are used to create RNAs in their functional forms.
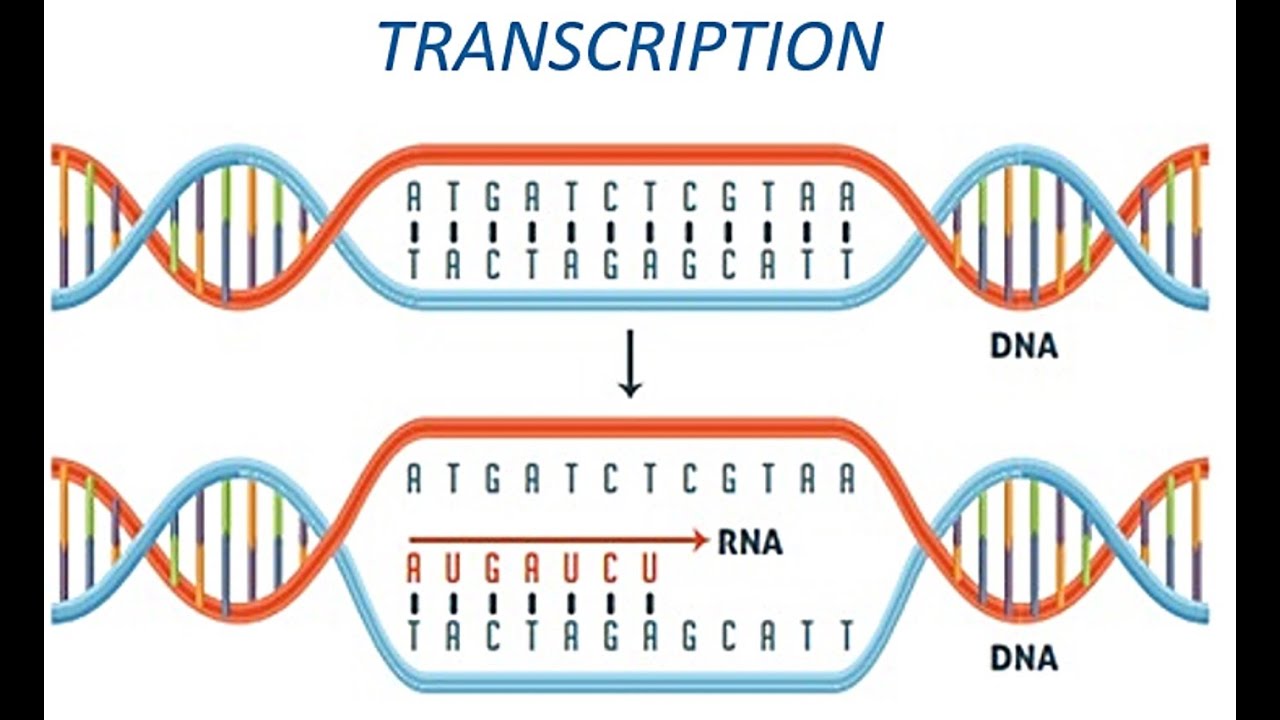
Translation makes it possible to synthesize proteins, which are essential in various bodily functions. Such copies are necessary for cellular biochemistry functions. Transcription is necessary for making copies of RNA of every gene. Below is the table that outlines the differences between transcription and translation. Transcription and translation processes are interrelated but they vary in functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
